
AC40 Support
Welcome to the product training for AC40 audiometer. On this page you will find an overview of all the available training materials and support.
Available Training
-
Synching Test Results to Diagnostic Suite
-
Accessing Saved Client Records
-
Saving Client Records
-
Load User Settings
-
Speech Settings
-
Common Settings
-
Setup Menu
-
How to Adjust Monitor Settings
-
Speech Display Screen and Function Keys
-
Tone Display Screen and Testing Functions
-
Keyboard Buttons
-
LCD Display Overview
-
Audiometer Overview
-
Hughson-Westlake Procedure
-
Masking Level Difference (MLD)
-
Threshold Equalizing Noise (TEN) Test
-
Alternate Binaural Loudness Balance Test
-
Quick Speech in Noise (QuickSIN)
-
Weber Test
-
Stenger Test
-
Pure Tone Audiometry
-
Speech Audiometry
-
Pediatric Noise
-
Tone Decay Test
-
High Frequency Audiometry
-
Short Increment Sensitivity Index
-
Audiometric Masking
-
How to print without a database
-
BKB-SIN speech-in-noise test
Békésy Audiometry
What is Békésy audiometry?
Békésy audiometry is an automatic method of measuring audiometric thresholds. It can be used for audiometric screening or in differentiation between the cause of the hearing loss e.g. non-organic hearing loss (Gelfand, 2009) or the origin of the damage in the ear (conductive, cochlear or retro cochlear) (James Jerger, 1962).
The patient being tested needs to hold down the response button when the tone is heard and release when the tone is no longer heard. When the response button is pressed, the intensity level of the frequency tested will automatically be reduced. When the response button is released, the intensity level will automatically increase. The patient’s response will be recorded as a trace on the Test Screen.
Required equipment
- Headphones or insert phones
- Patient response button
Békésy audiometry test procedure
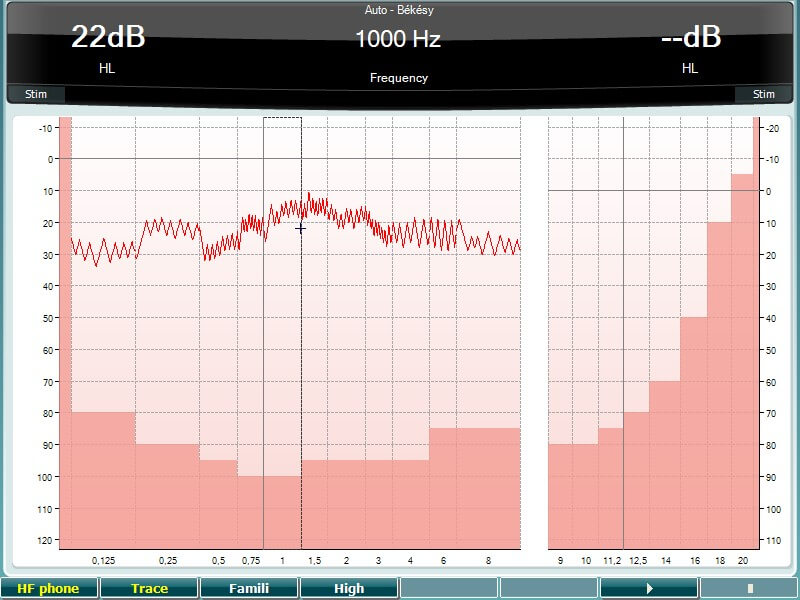
- Press and hold the Test button and use the black scroll wheel to select Auto – Békésy.
- Instruct the patient that he will hear some tones, which will vary in loudness and that he must press the response button as long as the presented tone is heard and let go when the tone is not heard.
- The tone is obtained with a continuous tone. To obtain the tracing with the pulsed tone, press the Single Multi button and ensure that Multi is selected.
Note the timing of the pulsed tone can be adjusted from the default setting by pressing and holding Setup, selecting Common and then reducing the Multi, pulse length slider. - To familiarize the patient with the test, press the button under Famili and press Play.
- To start the test, deselect Famili and select the button under Trace and press Play.
- Traces should be obtained for the desired audiometric test frequencies.
- To use the Békésy with different traces, complete the measure with a continuous tone and obtain the second trace with a pulsed tone (see example below).

Békésy audiometry results
When using the Békesy for clinical purposes, one threshold is obtained with a continuous tone and one with a pulsed tone. The results are interpreted based on the display of the continuous and pulsed tone.
Békésy Type 1: |
Continuous and pulsed tone overlapped, unknown pathology. |
Békésy Type 2: |
Continuous tracing slightly worse than pulsed tone tracing (Cochlear disorder). |
Békésy Type 3: |
Continuous drops off the graph as a result of adaptation to the tone (Retro cochlear disorder). |
Békésy Type 4: |
Continuous tracing is 20 dB lower that pulsed tone tracing (Cochlear or retro cochlear disorder). |
Békésy Type 5: |
Pulsed tone tracing below continuous tracing (feigning hearing loss). |
Setup
Setup │ Auto settings allows for changing the allowed deviation and number of reversals needed for a response to be stored.

References
Gelfand, S.A. (2009) Essentials of Audiology, Theime.
Jerger, J. (1962) Bekesy Audiometry, Hearing Tests in Otologic Diagnostics, ASHA May.
