ACT™ FAQ
Below, you can find quick answers to frequently asked questions on the Audible Contrast Threshold (ACT) test. For more detailed information, please refer to the Interacoustics Academy complete guide or the ACT quick guide.
Table of contents
- When do I perform ACT?
- What if I want to perform ACT in a follow-up session?
- Which clients can I perform ACT on?
- What happens if I have a client with no recordable responses in one ear or large asymmetry?
- Can I perform ACT on someone with tinnitus?
- Can I perform ACT on the pediatric population?
- Does ACT mean that I do not need to perform a speech‑in‑noise test?
- Is ACT a binaural test?
- What equipment do I need to perform ACT?
- Which software version do I need?
- Can I use ACT in simulation?
- Where do I find the ACT test in my software?
- How does the ACT stimulus work?
- How loud is the ACT test?
- What is the difference between the noise (reference stimulus) and the ACT signal?
- How can I recognize a false positive or false negative?
- What does ACT measure?
- What does nCL stand for?
- What does the ACT value mean?
- What should I do if the ACT value falls between two categories?
- How do I use the ACT value to adjust the hearing aid?
- Does ACT mean that I should not perform real-ear measurements?
- Can I use ACT regardless of the hearing aid brand?
- Will a client with normal hearing be able to hear a distinct difference between two ACT signals created from two very different audiograms?
When do I perform ACT?
It is recommended that you perform ACT directly after completing an audiogram. An audiogram is mandatory prior to completing ACT and this needs to be selected in the current session.
What if I want to perform ACT in a follow-up session?
To perform ACT in a follow-up session, follow these steps:
- 1. In the AUD tab, click on and highlight a previous session date of the chosen audiogram in the left-hand menu. Please note: the date should be highlighted as opposed to checking the box.
- 2. Go to Menu>Edit>Transfer to current session.
- 3. Ensure "Current session" is highlighted.
- 4. Go to Menu>Test>ACT. You can now perform ACT in a follow-up session.
Which clients can I perform ACT on?
You can perform ACT on anyone over the age of 18 who can complete pure tone audiometry. There may be cases where you may consider whether the test is appropriate for your client, such as in the following instances:
- Hyperacusis or severe tinnitus
- A severe-to-profound hearing loss
- Less cognitive capacity to focus during the test
Before performing ACT, please consider the client’s medical history alongside clinical judgement on whether you deem it suitable for your client.
What happens if I have a client with no recordable responses in one ear or a large asymmetry?
ACT can still be performed on individuals with significant asymmetric hearing losses. For instance, those with no recordable thresholds in one ear but measurable responses in the better ear can still be candidates for ACT. Although the test is conducted binaurally, clinicians can still derive a meaningful prediction of aided speech-in-noise performance based on how the client naturally perceives sound, which typically occurs in a binaural context.
A pop-up notification will indicate, "ACT stimulus not clearly audible due to severity of audiogram." It is important to note that all audiometers have an output limit, and since the ACT stimulus is an above-threshold test, profound hearing loss thresholds or no measurable responses prevents the audiometer from generating the output level required for those selected thresholds.
Can I perform ACT on someone with tinnitus?
ACT is an above-threshold test, but the risk to someone with tinnitus is low. You should always make a judgement based on your client’s symptoms and triggers.
Can I perform ACT on the pediatric population?
ACT studies have not been carried out with a pediatric population yet. The normative data is based on the adult population only and therefore, the recommendation is to perform ACT on clients over the age of 18.
Does ACT mean that I do not need to perform a speech‑in‑noise test?
ACT is a tool for predicting your client’s aided speech‑in‑noise ability. If you perform ACT, there is no need to do a speech-in-noise test unless your local protocol requires it.
Is ACT a binaural test?
ACT is a binaural test with each ear being presented with a signal based on pure tone audiometry. Cross hearing is not an issue for ACT.
What equipment do I need to perform ACT?
You will need:
- Affinity Compact or Callisto™
- Patient response button
- Connected PC and keyboard
- Headphones or insert earphones
- Licensed AC440 Audiometry module including an ACT license
Which software version do I need?
Your Affinity Suite software version must be at least 2.21. Your Callisto Suite software version must be at least 1.21.
Can I use ACT in simulation?
Yes, ACT can be used in simulation to review historic data only. An ACT test cannot be performed while in simulation mode.
Where do I find the ACT test in my software?
It is a test within the AUD module that you access in the same way as other AUD-based tests.
How does the ACT stimulus work?
A standard signal is presented for normally hearing adults. After conducting pure tone audiometry, the ACT stimulus is automatically adjusted to account for the hearing loss at frequencies between 250 Hz and 4 kHz for each ear. The ACT stimulus is a spectro‑temporally modulated sound imposed on top of bands of pink noise. The stimulus is non‑language specific but simulates the characteristic patterns of speech.
How loud is the ACT test?
The ACT test is automatically adjusted based on pure tone audiometry results. This means the ACT stimulus is clearly audible for all clients. For a person with normal audiometric hearing thresholds, the ACT stimulus is presented at 63 dB SPL, aligned with conversational speech. For clients with hearing loss, audibility is considered for each ear and each 1/3-octave band in the stimulus frequency range, with the stimulus shaped such that there is at least 15 dB of audibility in all 1/3-octave bands.
Please note, for this reason, we are unable to provide frequency-specific limits for each threshold of a given severe hearing loss. A message will appear in the software to indicate if the transducers are not able to produce 15 dB above the threshold. This will not stop you from performing ACT. Depending on the shape of the audiogram, the ACT value can still give you valuable information.
What is the difference between the noise (reference stimulus) and the ACT signal?
The reference stimulus and ACT signal are differentiated by whether there is modulation or not.
How can I recognize a false positive or false negative?
As in pure tone audiometry, some ACT runs may indicate inconsistent responses by the client. False positives (for instance, the client pressing the button too often) are automatically registered by the software and shown in the top right-hand bar of the ACT screen.
You can address false negatives (for instance, if the client does not respond to an ACT stimulus that they previously responded to, at the contrast level being tested) by altering the testing method. In the case of inconsistent runs, it can be helpful to deviate from the Hughson-Westlake (2 down, 1 up) procedure.
What does ACT measure?
The ACT diagnostic test is an above-threshold, non-language specific test that quantifies an individual’s real-world ability to hear in noise, with the intention of determining the level of help‑in‑noise needed from their hearing aid. The ACT test applies the shape and levels of a client’s audiogram to deliver an above-threshold stimulus (a siren-like sound) to objectively map their hearing-in-noise ability.
In other words, where the audiogram measures the quantity of hearing, ACT measures the quality of hearing. This makes ACT a robust assessment that reflects a person’s real-world hearing abilities.
What does nCL stand for?
nCL stands for normalized Contrast Level. It refers to the amount of modulation applied to the signal for the client to hear the contrast. This means, the higher the nCL value, the more contrast the client needs to hear it.
What does the ACT value mean?
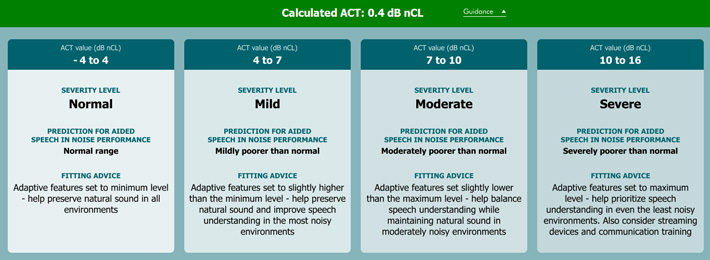
The ACT value denotes the level of contrast against the background noise a client needs to detect the ACT stimulus. A normal ACT value is between minus 4 and plus 4 dB nCL.
What should I do if the ACT value falls between two categories?
If the ACT value falls on a dB nCL value of 4, 7 or 10, we would recommend using the higher category at first fit and using follow-up appointments to collect your client’s feedback and adjust accordingly.
How do I use the ACT value to adjust the hearing aid?
The ACT value is designed to support the adjustment of advanced hearing aid features. Please refer to the guidance tab in the software (Figure 1).
Does ACT mean that I should not perform real-ear measurements?
You should still perform real-ear measurements. ACT will support you in setting the adaptive features of your client’s hearing aid. Real-ear measurements will support you in prescribing the correct dose of gain for your client.
Can I use ACT regardless of the hearing aid brand?
Yes. Some hearing aids can automatically use the ACT values. With those that can’t, you can make manual adjustments. To help with this, the software provides fitting guidance based on the ACT value (Figure 1).
Will a client with normal hearing be able to hear a distinct difference between two ACT signals created from two very different audiograms?
Yes. The frequency shaping is according to the loss.
