Getting started with the Eclipse Aided Cortical Module
This document serves as a quick run through on how to perform an aided cortical measurement. We refer to the Eclipse support page that contains the Additional Information and Instructions For Use documents for more information.
What is aided cortical testing?
Aided cortical testing is a cortical measurement performed in a free field setting while the patient is wearing their hearing aid(s) and/or cochlear implant(s). This test can also be performed without their device.
The purpose of performing aided cortical testing is to measure if the patient receives appropriate input from their hearing aid and/or cochlear implant(s) using speech-like stimuli, to assess their access to speech sounds using their device.
How to prepare the Eclipse and how to prepare your patient
First, open your EP software and choose the Aided Cortical protocol from the protocol dropdown list.
![]()
This protocol is set up and ready to use.
It is recommended to use sound field analysis before each session at the position where the patient will be tested to ensure the sound presented is correct, as changes in the room and patient placement can influence the intensity of the stimuli.
![]()
Refer to the Eclipse Additional Information document for more information about the sound field analysis.
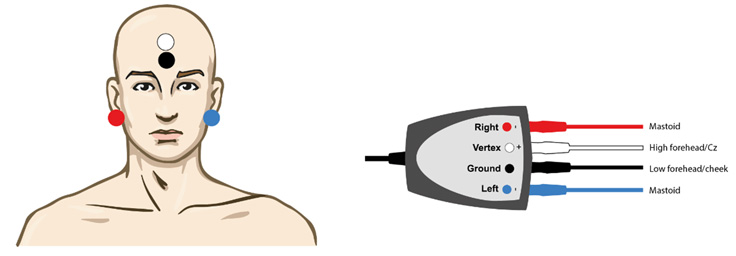
Second, clean the patient’s skin and mount the electrodes as you would with ABR, ASSR or ALR. Impedances below 5kOhm are recommended.
Third, if assessing a small child or infant, it is advised to have two clinicians present for the assessment, one to control the Eclipse, and the other to occupy the child. The patient should be engaged in activities involving for example toys or books to keep the patient awake and alert, while keeping them from paying attention to the stimuli.
Three types of stimuli are available to use:
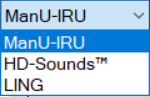
ManU-IRU consists of three speech-like stimuli created by the Interacoustics Research Unit, testing the low, mid, and high frequencies.
HD-Sounds™ consists of three speech-like stimuli created by Harvey Dillon, testing the low, mid, and high frequencies.
LING sounds consists of the six LING sounds.
For more information about different stimuli and features please refer to the Eclipse Additional Information document.
A short step-by-step example of the workflow
When you have prepared your patient, and they seem settled:
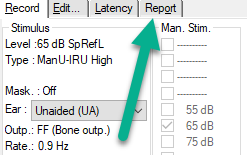
Select your stimulus, ear condition and intensity.
Press Start, and the freefield stimulation and recording will begin.
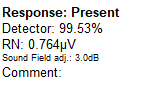
When you have your recording, turn to the Fmpi™ detector, as this will calculate the response confidence of the waveform. This acts as a useful tool for determining if a response is present or absent.
CR, RA and INC markers are available for you to place. Access to these labels is through right clicking the waveform handle. The marker will then be placed to the right of the waveform, as seen below.
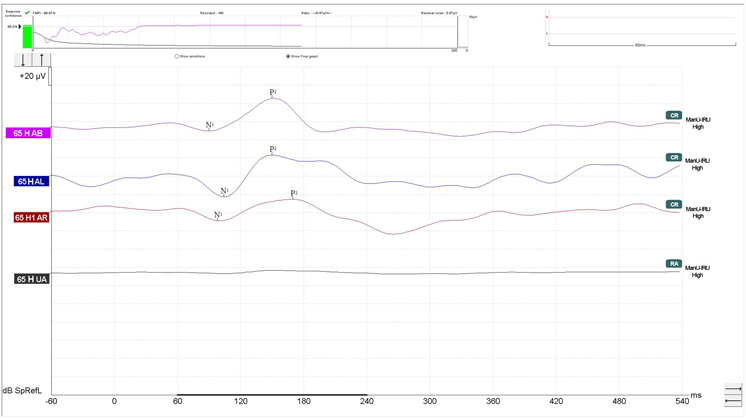
Aided cortical measurement using ManU-IRU stimuli investigating the higher frequencies.
These markers will automatically be put into a report, and so will the Fmpi value, sound field analyzer adjustment, residual noise value and comments on each waveform.
Tips for aided cortical testing
Tip: For adults, approximately 80-100 sweeps are typically acceptable to obtain good recordings.
Tip: For infants, 200-300 sweeps may be required to obtain good recordings.
Tip: Refer to the residual noise calculation and the Fmpi for an indication of the recording quality.
NOTE: when doing cortical measurements on infants, because their auditory system is not fully developed, their cortical responses will vary and will look quite different than on adults, therefore using the detector is recommended.
